Last Updated on May 2, 2024 by ACP JAPAN
In Japan, only the Importer of Record (IOR) is eligible to deduct input (import) consumption tax in principle.
The taxpayer liable for the Japan Consumption Tax on Imported Goods from the bonded area, and is considered the importer under Japanese customs law.
Under customs law, the importer is defined as the taxpayer, known as the “Importer of Record – IOR” (Customs Law Articles 6 and 7(1), Basic Customs Notification 7-1).
Since the Importer of Record (IOR) is liable for the tax on taxable goods, such an entity, as a business, is eligible to deduct the related Japan Consumption Tax under the Consumption Tax Law (Consumption Tax Law Article 30, Paragraphs 1(3) and (4)).
As of October 1, 2023, amendments to the Customs Regulations have tightened the definition of who can be an “Importer of Record (IOR)”. Only those involved in the transaction, such as buyers who import through sales transactions or those with ownership and disposal rights over the goods, are allowed. Third parties uninvolved in the transaction cannot be Importers of Record (IOR).
Foreign corporations without a physical presence in Japan (non-residents) can use our Attorney for Customs Procedures (ACP) service, allowing non-residents themselves to become Importer of Record (IOR) and deduct (or refund) import Consumption Tax. We have numerous experiences where we have facilitated such tax deductions (or refunds).
Case of Different Substantial Importer and Importer of Record
According to the Tokyo District Court decision on February 20, 2008, “In principle, a tax system where taxable entrepreneurs themselves deduct the taxes paid at the import stage should be assumed. Unless there are special circumstances, it should be understood that a plaintiff who is not the importer of record will not have their consumption tax deductible.” It indicates that tax declarations made in the name of a third party are not intended by law.
We can learn from this court case that only the Importer of Record (IOR) has the right to deduct input tax amounts.
In very limited cases, substantial importers who are not the formal Importer of Record are allowed to deduct input tax amounts.
Practically, it is appropriate to assume that entities who are not the Importer of Record (IOR) are not allowed to deduct import consumption tax.
An exception that allows the deduction of input tax amounts for those not being the importer of record exists under Basic Consumption Tax Notification 11-1-6 “Handling in Cases Where the Substantial Importer and the Importer of Record Differ”.
This directive states that even if the importer of record differs from the substantial importer, the following conditions, if met, allow the substantial importer to deduct the consumption tax paid on their taxable goods:
- The substantial importer sells the taxable goods to the importer of record (manufacturer, etc.) for a consideration after importing.
- The substantial importer bears the consumption tax amount related to the retrieval of the taxable goods.
- The substantial importer preserves the original import permit and receipt of the consumption tax related to the retrieval issued in the name of the importer.
Amendment of the Basic Customs Notification as of October 1, 2023
The revision to the Basic Customs Notification effective October 1, 2023, has tightened the definition of “importer = importer of record”, specifically:
- For goods imported through an Import Transaction (where the Japanese buyer becomes the importer via a sales transaction between an overseas seller and a Japanese buyer), the definition is similar to “person importing the goods” as stipulated in Basic Customs Notification 6-1(1).
- In cases other than the above, at the time of import declaration, it refers to those who have the authority to dispose of the imported goods after domestic retrieval, and if there are others performing the importing acts for the same purpose, it includes them as well.
In summary, if a non-resident or foreign corporation without an office in Japan wishes to import into Japan, it is naturally permissible for the Japanese buyer to become the importer via a transaction with a Japanese company, or for the non-resident having disposal rights to become the importer (using ACP, Attorney for Customs Procedures) and deduct import consumption tax. It is not permissible for a third party with no disposal rights or involvement in the transaction to act as the importer.
Foreign corporations without an office in Japan (non-residents) can use our Attorney for Customs Procedures (ACP) service to act as importers, allowing them to deduct import consumption tax (or, in some cases, obtain a refund). We have numerous instances where we have facilitated such tax deductions (or refunds).
JCT Compliance
Understanding the handling of JCT (such as payment of import JCT, collection of sales JCT from customers, and JCT returns) is crucial to avoid significant cost burdens. This is a vital aspect, so please ensure a thorough understanding to determine the most optimal business model.
Basic procedure
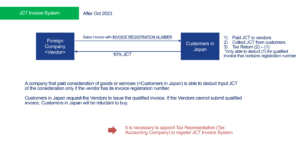
For non-resident entities (Company-A) that import and sell goods to customers in Japan, the standard procedure involves three steps:
- Pay import JCT to a customs office, 10% of the import customs value when Company-A imports goods. <PAY TO CUSTOMS OFFICE>
- Obtain JCT from customers in Japan, 10% of the sales price when Company-A sells goods.
- Submit JCT tax return and pay the difference amount (2) – (1) to a tax office periodically <PAY TO TAX OFFICE (different authority from Customs Office)>
Note: Using ACP to become the importer (IOR) is essential for JCT deductions and refunds. If another company acts as the IOR, you cannot deduct the input tax (step 1), and must pay the entire VAT collected (step 2) to the national tax authorities, leading to significant costs.
If you are a JCT-exempt business, the process ends at steps 1 and 2. For taxable businesses or invoice-registered businesses, step 3 (Final Tax Return) is obligatory.
In the Final Tax Return (step 3), if the JCT paid (step 1) exceeds the provisional JCT received (step 2), the difference is refunded. Conversely, if the provisional JCT received (step 2) exceeds the JCT paid (step 1), the difference must be paid to the tax office.
Why IMPORTER is important?
It is crucial to note that only the IMPORTER can deduct the import consumption tax at the time of tax filing. (= Deduct above (1) from (2) )
If Company-A uses another company to act IMPORTER, then Company-A can’t do above (3). Company-A has to pay all the amount of (2) to a tax office.
However, if Company-A imports goods using the Attorney for Customs Procedure (ACP), it becomes the Importer and can deduct the import consumption tax when filing the JCT tax return. In this case, Company-A only needs to pay the difference between the JCT collected from customers and the import JCT (2) – (1) paid to the Tax Office.
Appoint a tax accounting firm as Tax Representative / Tax Agent
Apart from utilizing ACP, when filing taxes in Japan (3), Company-A must appoint a Tax Representative. The Tax Representative will handle JCT tax registration and JCT filings with the tax office on behalf of the non-resident entity. SK Advisory can introduce our partner tax accounting company that can act as the Tax Representative.
Determination of JCT obligation (Taxable / Exempt)
Tax Payment Obligations of Nonresidents and Foreign Corporations
First, the consumption tax received from customers in Step 2 above should basically be paid to the national tax office. Consumption tax is imposed on transfers, etc. of assets made in Japan. Therefore, even if a nonresident or foreign corporation transfers assets in Japan, it is subject to consumption tax and is obligated to pay the tax.
In some cases, such as exempt businesses, it may not be necessary to pay the tax to the national tax office.
However, the following are examples where one cannot qualify as an exempt business and must file for consumption tax:
<Typical examples of businesses that are not tax-exempt and are required to file a consumption tax return
- Qualified JCT Invoice Issuer
- Businesses with taxable sales exceeding 10 million yen in the base period (roughly speaking, the fiscal year two years prior) for the taxable period
- Businesses with taxable sales exceeding 10 million yen for the specified period (roughly speaking, the first six months of the previous fiscal year, etc.)
- Newly established corporations (including specified newly established corporations) with capital or investments of 10 million yen or more for taxable periods without a base period
- Businesses that have made the election to become a taxable enterprise
※ With the amendments to the Consumption Tax Law in April 2024, regarding point 4, if a foreign corporation has capital or contributions exceeding 10 million yen when they start business operations in Japan (including specifically newly established corporations), regardless of when the corporation was established abroad, they are obliged to pay taxes and declare from the fiscal year they start operations in Japan (applicable for taxable periods starting after October 1, 2024).
If you’re an Exempted entity
During the exempt term, a new entity is not required to file tax returns. As long as your entity has exempt status, you are only required to:
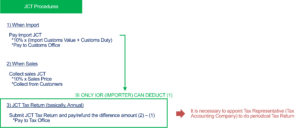
(1) Pay 10% tax of the import customs value when you import goods.
(2) Collect 10% of the sales price when you sell goods.
That’s all. You can enjoy the difference amount 2) – 1).
Can Tax-Exempt Businesses Receive Refunds?
Yes, it’s possible, but a final tax return (step 3) is necessary. Even if you’re an exempt business, you are still able to opt to submit a “Taxable Business Selection Notification” to the tax office, intentionally becoming a taxable business to file a final tax return and receive a refund for the paid import JCT. This is applicable only if the JCT paid at import (step 1) exceeds the provisional JCT collected (step 2). Note that using an ACP (Attorney for Customs Procedures) to act as the importer is essential for input tax deduction and refunds.
Japanese New Invoice System
Recently, many companies register JCT (Japanese Consumption Tax) because the new invoice system for JCT will start in October 2023. The concept of the new invoice system is very similar to the EU’s VAT invoice system.
Your Japanese customer can’t claim input tax credits unless the sellers(suppliers) issue a qualified invoice that is written a JCT number. To issue a qualified invoice, sellers(suppliers) need to be a taxable entity and get a JCT number.
Before the Invoice system is introduced (before Oct 2023):
- A company that paid consideration of goods or services (=Company-B) is able to deduct Input JCT of the consideration regardless of whether the vendor (issuer of invoice, =Company-A) is a JCT-taxable or Non JCT-taxable company.
- There is no way to confirm whether the vendor (=Company-A) is JCT-taxable or Non JCT-taxable company.
After the Invoice system is introduced (after Oct 2023):
- A company that paid consideration of goods or services (=Company-B) is able to deduct Input JCT of the consideration only if the vendor (Company-A) has its invoice registration number.
- Company-B requests Company-A to issue the qualified invoice. If Company-A cannot submit qualified invoice, Company-B will no longer want to buy from Company-A.
**If Company-A only sells to consumers (not business entities), it may not require for Company-A to issuethe qualified invoice since normally consumers would not tend to do tax return.
Once the Comapny-A (Seller/Supplier) obtains the JCT invoice registration number, which means this company becomes a taxable entity that is obligated to file JCT tax returns on a regular basis.
Is It Better to Become a Registered Invoice Issuer?
This depends on individual circumstances, but generally speaking, for B2B where customers are corporations, it’s better to be a Registered Invoice Issuer (as corporations file JCT returns and need qualified invoices for input tax deductions). For B2C where customers are primarily consumers, the necessity is somewhat reduced (as most consumers do not file JCT returns).
Many companies seem to become Registered Invoice Issuer without fully understanding the system. Being a registered business mandates the filing of a final tax return (step 3). Please seek advice from appropriate experts.
Is Support from a Certified Tax Accountant Necessary?
For non-residents conducting tax office procedures (step 3) in Japan, appointing a Tax Representative is required. The ACP handles customs procedures, while the Tax Representative deals with national tax (tax office) matters. Under the Certified Tax Accountant Act, the following tasks are exclusively performed by the Certified Tax Accountants, making their support essential:
- Preparation of tax documents
- Tax representation
- Tax consultation
Our company, in partnership with Certified Tax Accountants skilled in international taxation, will provide support in these areas.
Japanese Customs System Reform: Clarification of Importer Definitions
Starting October 1, 2023, Japanese Customs has instituted a pivotal reform aimed at addressing the issue of foreign sellers improperly designating third parties (such as forwarders or customs agents) as importers.
This revision necessitates foreign corporations to utilize an Attorney for Customs Procedures (ACP) to assume the role of Importer of Record (IOR) directly in many cases. The practice of merely nominally appointing another entity as the importer is no longer feasible.
Notably, foreign corporations that act as importers themselves, through the engagement of ACP, are eligible for Japan Consumption Tax (JCT) benefits. (link: Consumption Tax Treatment and Benefits of Using ACP).
As a dedicated ACP firm, we ensure compliance with the law to facilitate correct import procedures, allowing you to trust us with your importation requirements confidently. We are eager to engage in further discussions with you.
Revisions Effective October 1, 2023:
Definition of the Importer
- Regarding a cargo imported under import transaction, an importer is equivalent to “a person who imports a cargo” defined in Article 6-1 (1), General Notification of the Customs Act. ….. This means, the Consignee, etc., in the case of imports conducted through normal transactions between an overseas seller and a Japanese buyer
- In the cases other than above, an importer is a person who has a right to disposition of the import cargo at the time of import declaration. If there is another person who acts on the purpose of the import*, that person is also included :
In case of a cargo imported:
– under lease contracts, a person who rents and uses the cargo.
– for consignment sales, a person who sells the cargo in the name of himself/herself (consignee) by accepting the commission.
– for processing or repairing, a person who processes or repairs the cargo.
– for disposal, a person who disposes the cargo.
For additional information, please refer to the following resources:
- Japan Customs: Leaflet(English) Revision of Import Declaration Items and Attorney for Customs Procedure (ACP) System
- English: Announcement from Japan Customs | Mandatory to Use ACP in Many Cases – Attorney for Customs Procedure
Our ACP Service: The Best Solution for the Japan Importer of Record (IOR) and Exporter of Record (EOR)
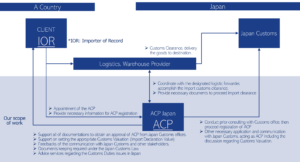
Attorney for Customs Procedures (ACP) is the best solution for addressing the issue of Japan IOR – Importer of Record. Below is an outline of our primary services and a diagram illustrating the operational structure of the ACP service. Upon successful ACP registration, a foreign entity can become the Japan IOR – Importer of Record.
Basic Scope of Services:
- Consultation with the Japan Customs Office for successful ACP registration.
- Liaising with stakeholders, including Logistics Forwarding Companies and the Customs Offices, on behalf of non-resident clients (i.e., non-resident Japan IOR) to ensure the secure importation of goods.
- Assistance in preparing the necessary documentation for import clearance.
- Support of calculation of Customs Value (Customs Valuation Formula), in accordance with appropriate compliance under the Japan Tariff Customs Law.
- Security Export Control (Classification for List Control, Examination for Catch-All Control, Application of the license to Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry)
- Documents keeping, required under article 95 – Japan Customs Law
- Providing professional trade/customs advice if any issues arise.
**Both import and export activities can benefit from the use of an ACP (Attorney for Customs Procedures). This support is applicable in scenarios where a non-resident acts as the Importer of Record (IOR) for imports and as the Exporter of Record (EOR) for exports.
Three Steps to Initiate Shipments Under the ACP Program: :
- Quotation Review to Contract Conclusion: Upon receiving your contact details, we will promptly provide a quotation for your review.
- Commencing the Registration of ACP (Attorney for Customs Procedure) to Japan Customs: This process is generally completed in about two weeks.
- Initiation of First Shipment, Import/Export
Our Customers – Japan IOR / Attorney for Customs Procedures (ACP) Service
All our clients have successfully become Japan Importer of Record (IOR) and imported goods into Japan under our guidance.
Logistics Companies with Collaboration Experience
Here is a list of our partner logistics and forwarding companies with whom we have had successful collaborations. Please note that this list is not exhaustive, as we are open to working with any logistics or forwarding companies. As Attorneys for Customs Procedures (ACP), we represent non-resident clients (IOR) and coordinate with these logistics companies, who manage the transportation of goods to and from Japan.
Please Be Careful
In cases where foreign corporations (non-residents) without an office in Japan import goods, failure to properly prepare an Importer of Record (IOR) through an Attorney for Customs Procedures (ACP) or similar means can result in goods being held at customs, leading to significant delays and costs. To avoid such risks, please make thorough preparations.
If an ACP is needed, it is crucial to utilize the services of an experienced ACP well-versed in customs-related laws and regulations. The import and export operations of non-residents/foreign corporations using an ACP are treated as unique cases. Many customs brokers are not familiar with these procedures, leading to incidents where goods are detained for extended periods due to unsuccessful explanations to customs. (Customs will not permit the import if the explanations provided by the importer or customs broker are unsatisfactory, resulting in the goods being detained until customs is convinced.)
We highly recommend utilizing our services as professional experts in customs, knowledgeable about customs-related laws and regulations. With a proven track record of resolving numerous issues through direct consultations with customs officers and customs brokers, our clients supported as an ACP now exceed 100 companies. We are committed to delivering industry-leading results with our expertise.
Why choose us?
- Customs and International Trade Professionals – Our CEO, Mr. Sawada, is a Certified Customs Specialist in Japan. With years of experience providing services in the Trade & Customs field, his leadership at KPMG and the establishment of his own company, SK Advisory, ensures our commitment to excellence and high-quality service.
- Full Adherence to Japanese Customs Law – Our top priority is to maintain full compliance with Japanese Customs Law and safely import / export our clients’ goods into / from Japan. We meticulously manage all import compliance aspects, including Japan Importer of Record (IOR) matter, HS code classification and the correct Customs Valuation of goods entering Japan. We support to complete all the necessary shipping documents, such as Invoice, Packing List and BL, on behald of non-resident / foreign Japan IOR.
- Communication in English, Chinese, and Japanese – Our team, with extensive international experience, excels in communication in English, including facilitating English-language meetings, and has earned considerable trust from clients. We also have staff capable of communicating in Chinese, making us equipped to handle Chinese-language support as well. Naturally, as a Japan-based team, we’re totally fluent in Japanese, ensuring seamless communication across these three key languages.
- Reputable and Reliable Partner -The growing demand for our Attorney for Customs Procedures (ACP) services is testament to our quality. We proudly serve clients globally, registering over 50 ACP customers annually. Our consistent track record underscores our reliability and credibility. Our unwavering commitment ensures all our clients successfully acquire Japan IOR status and import goods seamlessly into Japan.
- Handling Regulated Products – Our ACP/IOR partnership system can manage regulated items, including cosmetics, PSE-products, foodstuffs, and tableware.
- Recognized ACP Service Provider on Amazon SPN (Service Provider Network) – We are a certified ACP service provider within Amazon’s Service Provider Network (SPN), listed under the Trade Compliance category. Many international Amazon Sellers have successfully become Japan Importers of Record (IOR) through our ACP services.

Restrictions on Handling by ACP in Japan – Our System Enables Us to Handle Regulated Items
Japanese Certain laws, such as the Pharmaceutical and Medical Products Act, the Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Act (PSE), the Consumer Product Safety Law (PSC), and the Food Sanitation Act, stipulate that importers must be corporations with a registered address in Japan, and thus restrict handling.
However, we have established a partnership system that enables us to arrange the Importer of Record (IOR) and Attorney for Customs Procedures (ACP) for regulated items, including cosmetics, PSE-regulated products, foodstuffs, and tableware.
While many ACP service providers do not handle such regulated items, our ability to handle those regulated items has become a competitive advantage of our company. Please consult with us for handling these regulated items.
How to determine the Import Declaration Value?
Primary determination method
The process of determining the Import Declaration Value of imported goods is known as “Customs Valuation.” In most cases, when an import is based on an “Import Transaction”※1 between an overseas seller and a buyer in Japan, the primary determination method can be utilized.
※1:An “Import transaction” refers to a transaction where a buyer in Japan engages in a sales transaction with an overseas seller for the purpose of shipping goods to Japan, and the goods subsequently arrive in Japan.
Under the primary determination method, the Customs value of the imported goods is determined as the transaction price paid by the buyer (CIF basis).
Customs Duty is calculated by multiplying the Customs Value (Transaction Value) by the Duty Rate, which varies depending on the HS code of the goods.
Consumption Tax, on the other hand, is calculated by multiplying the Customs Value plus Customs Duty by the Consumption Tax rate (currently 10%).

Exceptional determination method (e.g. when to use ACP)
In cases where a non-resident company imports goods into Japan without engaging in a sales transaction, the primary method cannot be utilized. Simply using an Invoice Value is not appropriate.
To calculate the Customs Value in such situations, it is necessary to apply the Exceptional Determination Method.
Within the exceptional determination method, several methods can be considered:

- Transaction Value of Identical or Similar Goods Method: If you have previously imported goods that possess identical or similar conditions to the goods in question, the transaction value of those goods can be used.
- Domestic Selling Price Method (Deductive Method): If you can identify the sales price (can be an estimated sales price), the domestic selling price method can be employed.
- Cost of Production Method (Cost plus Method): If the exporter is a manufacturer and can provide production costs, the production cost method may be applicable.
If none of the above methods are suitable, “Other methods” are utilized as a flexible determination method, taking into account the calculation methods mentioned earlier.
In the practical scene, most of the cases we use this “Other methods” which is a determination method in a flexible way through considering the previously mentioned calculation methods.
Avoiding Customs Valuation Problems
In recent times, there have been numerous instances of trouble arising from incorrect Customs Value settings.
In the worst-case scenario, goods may fail to clear customs, resulting in significant detention fees and eventual return shipment.
At SK Advisory, we specialize in establishing appropriate Customs Values. We can assist in conducting consultations with Japan Customs on behalf of our clients, effectively avoiding any potential issues down the line.
For Amazon’s FBA business, there is a recommended calculation formula for the declaration value. If you would like to learn more about it, please don’t hesitate to contact us!
FAQ for ACP (Attorney for Customs Procedures)
What is the role of ACP (ACP Japan)?
- Representation: ACP (ACP Japan) represents the foreign importer and liaises with Japan Customs and the Forwarding Company/Customs Broker.
- Documentation and Compliance: ACP assists in preparing essential import documents (e.g., Invoices) in compliance with Japan Customs Law and formally requests the Customs Broker to proceed with customs clearance.
- Expert Consultation and Troubleshooting: We are a team of legal experts in Customs Laws, providing direct consultations with Japan Customs to ensure compliance and address issues, including troubleshooting unique challenges in non-resident imports.
How long time does it require to get ACP’s registration?
It will take approximately 2 weeks until getting an approval from Japan Customs Office.
The breakdown of the task is as follows.
- Prepare the necessary documentation between us
- Start pre-consultation with Japan Customs Office and proceed initial review
- Submit paper-based set of application documents to Japan Customs Office for final review
What kind of documents to be necessary for ACP application?
Not limited, but for instance – Power of Attorney, Company Registry, The calculation method of Customs Valuation, Catalog of the import goods, business/logistic flow
ACP can handle all kinds of goods?
Whereas many ACP service providers do not handle regulated items, our company’s competitive advantage stems from our ability to manage such products. We can support regulated items, including cosmetics, PSE-regulated products, foodstuffs, and tableware.
Which regions in Japan are we covering?
Any region in Japan, we can handle.
What is difference between ACP and IOR?
ACP is not the Importer. ACP enables non-resident entities to become IOR (Importer of Record).
—
We’re a reliable ACP service provider for Amazon FBA’s seller
In recent, we’ve been supporting many import projects of goods related to the Amazon-FBA program. If you are looking for a reliable ACP service provider, please let us know.
—
Guidance by Amazon
According to the seller central website in Amazon, there is guidance by Amazon that a non-resident entity needs to appoint an ACP or IOR. You may check on this “Non-resident requirements”. Also, you can check the document developed by Amazon “Understand ACP and IOR guidance”. —–
Our ACP Service (Attorney for Customs Procedures)
—–
[Our Service]
Our ACP Service for Importer of Record (IOR)
Our ACP Service for Exporter of Record (EOR)
[Knowledge Pages]
What is ACP? – Attorney for Customs Procedures
Steps of using ACP, how foreign entity can import into Japan by ACP
What is IOR? – Importer of Record
Customs Valuation System in Japan
Customs Valuation When You Import By ACP
Limitation on Handling by ACP in Japan – Our System Enables Us to Handle Regulated Items
[Recent Updates]
ACP Japan Became Amazon’s SPN Provider as Qualified ACP Service Provider
Taxes on Imports: Customs Duty and Japan Consumption Tax (JCT)
Import Permit Document and Alert on IOR Service
New Japan Qualified Invoice System and import JCT (Japan Consumption Tax)